|
|
>>
New User Register 

Login Member:
|
|
|
|
| The most in-depth interactive & animated coverage of virus ever, covers- what are viruses?, their structure, genome, capsid, envelope, characteristic features, pathogenic nature, difference between viruses and cellular pathogens, viroids and prions, classification, where are viruses found?, their discovery, studying viral structure, significance of viruses.
|
Virus
This animation has audio.
Category : Microbiology
- virology
Type : Animation
Animation Type : Advanced
Total animation length: 2
Hours or more
The animation covers:
- What are viruses?
- Structure of virus
- Viral genome or Nucleic acid
- Protein coat or capsid
- Envelope
- Characteristic features of viruses
- Pathogenic nature of viruses
- Difference between viruses and cellular pathogens
- Viroids and Prions
- Classification of viruses
- Where are viruses found?
- Discovery of viruses
- How is virus structure studied?
- Significance of viruses
|
|
| Click
on link below each image to view a bigger one or see
preview |
|
|
 |
| Bigger
Image |
Bigger
Image |
| Virus envelope,
capsid and nucleic acid are separate animated sections.
Capsid animation is a unique one, it shows the assembly
of capsid from proteins. |
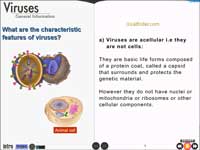
Characteristics
features of virus - Explains both living and non-living
characteristics of a virus.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Classification of virus - on
the basis of : nature of viral genome, structure of
genome,
capsid symmetry, envelope, replication.
|
Viral genome or Nucleic acid -
Covers DNA, RNA, wider range of genomic variety.
|
|
|
|
| Bigger
Image |
Bigger
Image |
|
Types of viruses : Description
of tobacco mosaic virus, adenovirus, poliovirus, bacteriophage,
ebola, small pox virus
|
Viral structure -
nucleic acid - click to see the content of animation
or look at preview to know more |
|
This 2-hour animation is an in-depth and comprehensive
approach towards virus. Virology itself is a big topic-
this is the part 1 of the triology, the other two parts
Virus- lifecycle ( Replication ) and Viral - immunity are
presently under development and will be released shortly.
Short Description:
What are viruses?
Viruses are microscopic entities capable of infecting virtually
all life forms. Can be viewed only through electron microscope.
Their size ranges from 20nm -300nm.
Structure of virus:
A virus's body contains
-Nucleic acid packed in protein coat capsid.
-Capsid may be surrounded by a bilipid envelope.
Viral genome or Nucleic acid
The genome of a virus
-DNA or RNA.
-Wider range of variety in their genomes
Protein coat or capsid
Capsid- made up of proteins.
Smallest subunit - a protein molecule or polypeptide chain.
Assembly- protomer - one or more proteins.
Morphological or symmetrical unit - Capsomer - one or more
protomers.
Capsid and genome together - Nucleocapsid
Capsid symmetry-shape of virus-Icosahedral symmetry (Adeno,
Retro)
- helical symmetry (influenza, Rhabdo)
- Complex symmetry (bacteriophage T4, Pox virus)
Envelope - not all viruses have envelope
Enveloped virus - appear mostly spherical (HIV), bullet
shaped (Rhabdovirus) or brick shaped( pox virus)
Non enveloped virus - adenovirus, Tobacco mosaic virus
Envelope made up of
Lipids derived from host cells with
Viral proteins -
-- Surface glycoproteins that appear as spikes
--Transmembrane proteins
--Embedded in the lipid layer.
Characteristic features of viruses - Virus possesses
both living and non-living characteristics.
- Acellular organisms
- Do not grow or divide
- No metabolic activities
- Inert, inactive in the environment
- Obligate intracellular parasites i.e. replicate or reproduce
only within a living cell.
Pathogenic nature of viruses:
All viruses are pathogens to some or the other living organism.
- Viruses are as good as a dust particle in the environment
- But all viruses bounce into action when come in contact
with a specific living cell, take over the cellular machinery
and directs the cell to produce virus progeny leading to
cell lysis or malfunctioning of the cell, thus causing disease
in infected organisms. A few viruses stimulate cells to
grow uncontrollably and produce cancers.
Difference between viruses and cellular pathogens:
Comparing microrganisms like bacteria, fungi, protozoans,
helminths and viruses
Viroids and Prions:
Not viruses, but virus like particles: Viroids are ultramicroscopic,
single-stranded molecules of RNA without any protein coat.
They infect plants.
Prions are proteinaceous infectious particles, cause degenerative
diseases in animals
-e.g., scrapie in sheep
-bovine spongiform encephalopathy in cattle
-Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in humans
Classification of viruses: Viruses are classified
on the basis of their following properties:
-Nature of viral genome: RNA or DNA
-Structure of genome : double or single stranded, linear
or circular
-Capsid symmetry: icosahedral, helical or complex
-Presence or absence of envelope
-Replication strategies
Where are viruses found?
-Everywhere
-Evolved to infect all organisms from humans to bacteria.
-Highly host specific.
Grouped into the following:
--Plant viruses
--Animal viruses
--Bacteriophages
Discovery of viruses:
- Platform to the discovery of viruses:
In 1880 Mayer identified an infectious agent in tobacco
leaves that could transmit the infections into a healthy
new plant.
In 1892 a Russian scientist Dimitri Ivanofsky discovered
that the infectious agent of tobacco leaves was filterable
claiming that agents are smaller than bacteria.
1898, Beijerinck referred to this new disease agent as a
contagious living liquid-contagium vivum fluid.
In 1935 Wendell Stanley crystallized tobacco mosaic virus
to demonstrate that viruses had regular shapes, and in 1939
tobacco mosaic virus was first visualized using the electron
microscope.
How is virus structure studied?
Tools applied in studying the structure of virus include:
Electron microscopy
X-ray crystallography
Atomic force microscopy
Significance of viruses:
Viruses are simple biological entities and are therefore
important to the study of molecular and cellular biology.
- Study of viruses helped our understanding of the basic
mechanisms of molecular genetics.
- Viruses are used as a tool to cure bacterial infections
and are now used in curing genetic disorders.
- Used in producing vaccines against viral diseases.
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|

