
Electrons are the negatively
charged subatomic particles. They have negligible mass of
about 9.1 * 10(-31) Kg and a charge of 1.6*10(-19) C.
Sir John Joseph Thomson first discovered the electron in
1897 while studying the nature of cathode rays.
The cathode rays were a subject of interest from over
almost two centuries.
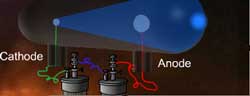
It was observed that whenever the glass tube filled with
air at low pressure and sealed with electrodes at both the
ends was subjected to about 10,000 volts of electricity,
a strange glow was produced around the edges of the wide
end of the glass tube, irrespective of the type of gases
present in it. (The glass tube with sealed electrodes
is called discharge tube.)
Many Scientists like Faraday, Goldstein, Perrin, Crooke,
and Hertz investigated on the properties of the cathode
rays.
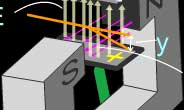
The properties of the cathode rays that they discovered
during the experimentation was that:
- They were produced by the negative electrode, or cathode,
in an evacuated tube, and traveled towards the anode.
- They travel in straight lines and cast sharp shadows.
- They have energy and can do work.
- They were deflected by magnetic fields
Though the properties were known, the nature of the particles
was still unknown. In fact the scientific community was
divided into two groups one group believed that cathode
rays as nothing but corpuscles (particles) while the other
group believed it to be an electromagnetic wave.
In 1897, SirJ.J. Thomson, drawing on work of his colleagues,
studied the nature of cathode rays.

For studying the properties of cathode rays, he improved
the discharge tube by completely evacuating it and performed
three sets of experiments on the beam of cathode rays:
He first subjected the cathode rays to an electric field
and then to a magnetic field individually. The remarkable
achievement for him was that he could not only bend the
rays in the presence of magnetic field but also could successfully
bend the rays in electric field.
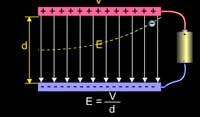
This led to the conclusion that cathode rays are not
electromagnetic waves because electromagnetic waves
are not affected by either magnetic field or electric field.
He concluded that they are nothing but charged corpuscles
(particles).
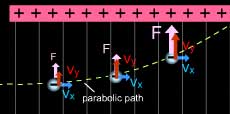
Further the deflection of rays towards the positive plate
led him to the conclusion that they are beam of same kind
of particles with a negative charge.

To determine the charge to mass ratio of the particles he
then subjected the beam to simultaneous crossed electric
and magnetic fields perpendicular to the direction of the
motion of the particles.
He initially switched off both the fields and noted the
equilibrium position.
He then switched off the magnetic field and noted down the
deflection point of the cathode rays in the presence of
only electric field. He noted down the deflection.Then he
applied the magnetic field in such a way that the cathode
rays were brought back to the equilibrium position.
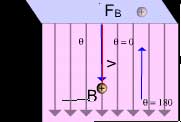
Now at equilibrium position, the electric and magnetic force
on the charged particle are equal. Using the equations of
motion he calculated the velocity of the particle.
He then carried out the calculations to determine the specific
charge (e/m) ratio of the particles.
He named these particles as electrons. (The word 'electron'
first used by G. Johnstone Stoney in 1891 had been used
to denote the unit of charge found in experiments that passed
electric current through chemicals.)
J. Thomson confirmed that an almost constant value of e
/m was always obtained under various experimental conditions
and even for different gases and metals. He therefore concluded
that the cathode rays are a collection of the same kind
of particles.
The e/m value was found to be 1.76 * 10(11) C/Kg.
He compared this value with the value of hydrogen atom and
found that the mass of these particles were less than that
of the hydrogen atom (lightest element on earth).
This led him to the conclusion that the electrons are constituents
of the atoms and thus atoms are divisible.
If you are still unclear about
the concepts, please refer the animation
Besides the above details the animation file also contains
the following in detail
The animation also contains history of discharge tube,
behavior of charged particle in electric and magnetic field
|

